- Internal Force: When an external force is applied to an object, deformation and resistance occur simultaneously, creating a balance with the external force.
- Stress: The magnitude of internal force per unit area
1. Normal Stress (also known as Axial Stress): The stress acting perpendicular to the material surface.
A. Equation: Normal stress = Load, Internal force, External force/Area = P/A [Pa(N/m^2), MPa(N/mm^2)] [1000000Pa = 1000KPa =1MPa]
B. When a tensile stress is applied and the specimen extends, it is generally marked as (+).
C. When a compressive stress is applied and the specimen shrinks, it is generally marked as (-).

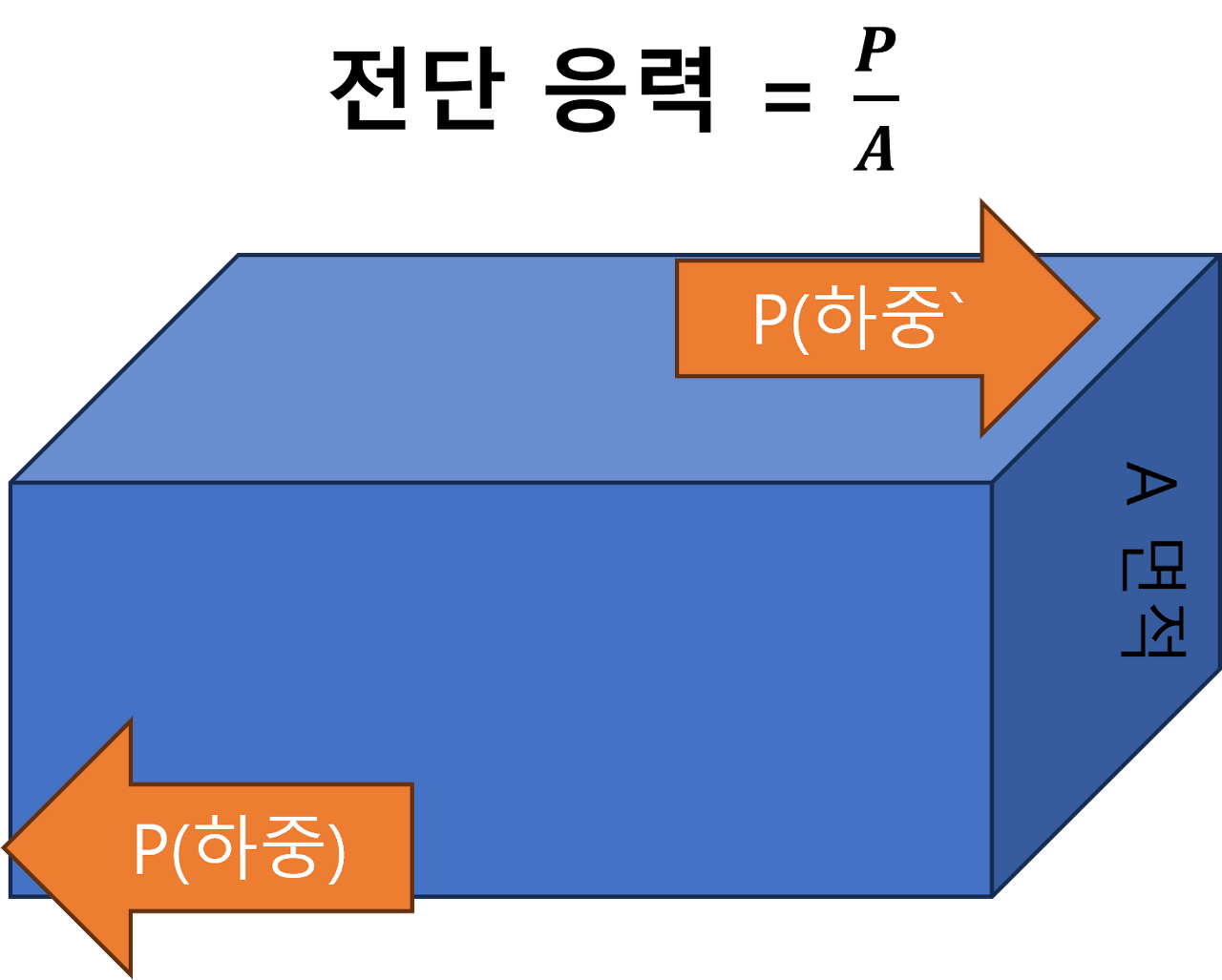
2. Shear Stress: The stress that occurs in the tangential direction along the section.
A. Equation: Tau = τ = P/A [Pa(N/m^2), MPa(N/mm^2)]
- Strain: The ratio of deformation of a material due to load.
1. Longitudinal Strain: The strain caused in the longitudinal direction by a load in the length direction.
A. Equation: ε = (l'-l)/l = λ/l

2. Transverse Strain (Compression Strain): The strain caused in the transverse direction by a load in the length direction.
A. Equation: ε' = (d'-d)/d = δ/l (where d': contracted length, d: horizontal length)
3. Shear Strain: The strain of an object under the influence of shear stress.
'역학 > 고체역학(재료역학)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 재료역학(고체역학): 탄성(Elasticity)과 소성(Plasticity) (0) | 2024.02.10 |
|---|---|
| 재료역학(고체역학): 연성(Ductility)과 취성(Brittleness) (0) | 2024.02.09 |
| 재료 역학(고체 역학): 변형률(Strain)이란? (2) | 2023.12.12 |
| 재료 역학:재료의 강도 실험: 인장 시험과 압축 시험의 이해 (0) | 2023.12.09 |
| 재료역학: 기존 응력의 사용 제한 조건 알아보기 (0) | 2023.12.08 |